Enzymes Involved in Dna Replication
It helps in the polymerisation catalyses and regularises the whole process of DNA replication with the support of other. In response to the molecular cues received during cell division these molecules initiate DNA replication and synthesize two new strands using the existing strands as templates.

Steps And Proteins Involved In Dna Replication Dna Polymerase Dna Ligase Mitochondrial Dna
One of the two.

. This article covers the Enzymes Involved in DNA Replication. The process of DNA replication is a complex one and involves a set of proteins and enzymes that collectively assemble nucleotides in the predetermined sequence. The enzyme is now ready to make a strand of mRNA with a complementary sequence of bases.
Initiation of DNA Replication. Molecular mechanism of DNA replication. Transcription Produces RNA Complementary to One Strand of DNA.
Leading and lagging strands and Okazaki fragments. A break in both complementary strands of DNA. The two DNA strands are separated by the DNA helicase.
The central enzyme involved is DNA polymerase which catalyzes the joining of deoxyribonucleoside 5-triphosphates dNTPs to form the growing DNA chain. As discussed in Chapter 3 DNA replication is a semiconservative process in which each parental strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary daughter strand. RNA polymerase reads the unwound DNA strand and builds the mRNA molecule.
For eg if it. DNA ligase is a specific type of enzyme a ligase EC 6511 that facilitates the joining of DNA strands together by catalyzing the formation of a phosphodiester bondIt plays a role in repairing single-strand breaks in duplex DNA in living organisms but some forms such as DNA ligase IV may specifically repair double-strand breaks ie. Among them DNA-dependent DNA polymerase is the main enzyme.
Roles of DNA polymerases and other replication enzymes. Other proteins are also involved for initiation of the process and copying of DNA along with proofreading capabilities to ensure the replication process takes place accurately. All of the RNA in a cell is made by DNA transcription a process that has certain similarities to the process of DNA replication discussed in Chapter 5Transcription begins with the opening and unwinding of a small portion of the DNA double helix to expose the bases on each DNA strand.
In prokaryotes DNA replication takes place in the cytoplasm whereas in eukaryotes DNA replication occurs in the nucleus during the S-phase of the cell cycleDuring initiation the DNA is made accessible to the proteins and enzymes that are involved in the replication process. Speed and precision of DNA replication. There are many enzymes involved in DNA replication which includes the enzymes DNA-dependent DNA polymerase helicase ligase etc.
The replication of DNA begins at a point known as the origin of replication. This is the currently selected item. During transcription enzymes called RNA polymerases build RNA molecules that are.
The Cell Structure and Functions Synopsis Points. However DNA replication is much. DNA polymerase III reads the nucleotides on the template strand and makes a new strand by adding complementary nucleotides one after the other.
On the leading forward strand the DNA is synthesized continuously. This forms the replication fork. This signals the DNA to unwind so the enzyme can read the bases in one of the DNA strands.
Transcription is the first step in decoding a cells genetic information. On a cellular level this reproduction occurs by mitosis the process by which a single parental cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells. Leading and lagging strands in DNA replication.
Helicases are often used to separate strands of a DNA double helix or a self-annealed RNA molecule using the energy from ATP hydrolysis a process characterized by the breaking of hydrogen bonds between annealed nucleotide basesThey also function to remove nucleic acid-associated proteins and catalyze homologous DNA recombination. DNA replication process uses DNA polymerase as the main enzyme for catalyzing the joining of deoxyribonucleoside 5-triphosphates dNTPs forming a growing chain of DNA. Elongation is the addition of nucleotides to the mRNA strand.
Formation of the Replication Fork The polymerase III holoenzyme binds to template DNA as part of a multiprotein complex DNA polymerases only synthesize DNA in the 5 to 3 direction Because the DNA strands are antiparallel the polymerase functions asymmetrically.

Image Result For Dna Replication And Enzymes Biologia
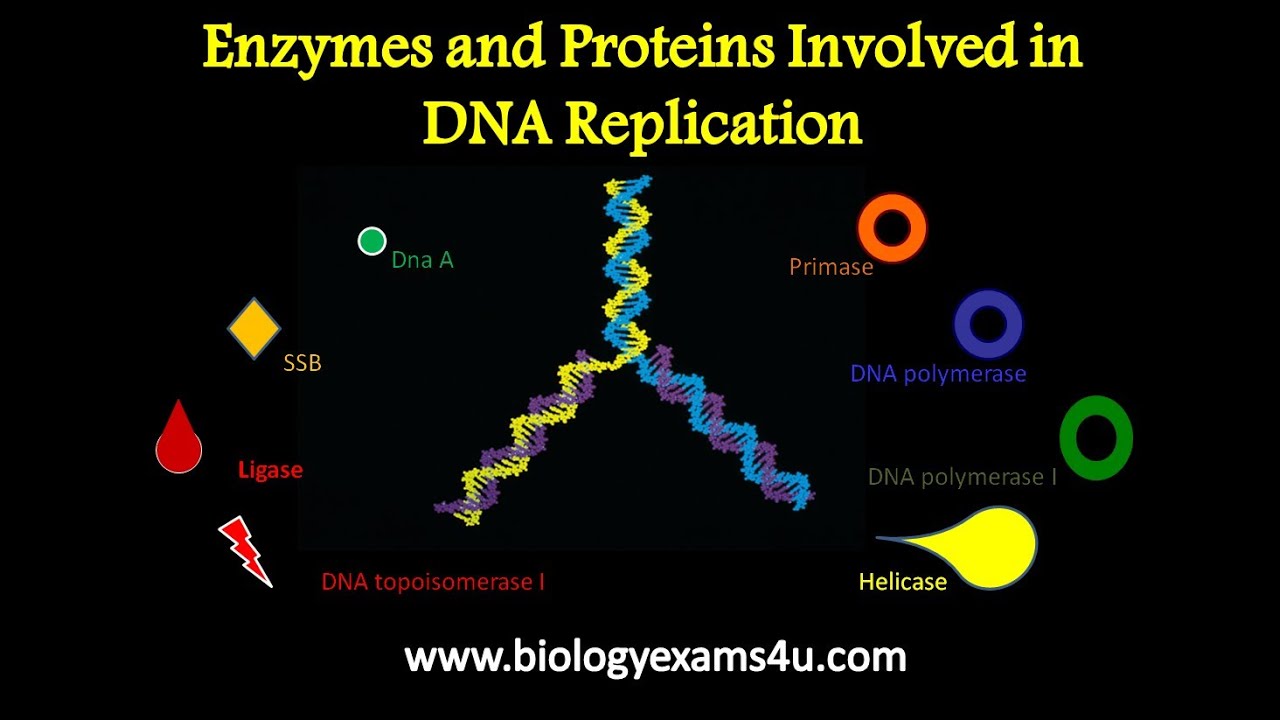
Enzymes And Proteins Involved In Dna Replication And Their Functions Biologia

Dna Replication In Prokaryotes Process And Enzyme Involved In Replica Dna Replication Prokaryotes Dna

Comments
Post a Comment